Saliency Detection Via Similar Image Retrieval
Linwei Ye1 Zhi Liu1 Xiaofei Zhou1 Liquan Shen1 Jian Zhang2
Image and Video Processing LAB,Shanghai University1
Global Data Technologies Centre, School of Computing and Communication, University of Technology, Sydney, Australia2
Abstract
This paper proposes a novel saliency detection framework by propagating saliency of similar images retrieved from large and diverse Internet image collections to boost saliency detection performance effectively. For the input image, a group of similar images is retrieved based on the saliency weighted color histograms and the Gist descriptor from Internet image collections. Then a pixel-level correspondence process between images is performed to guide the saliency propagation from the retrieved images. Both initial saliency map and correspondence saliency map are exploited to select the training samples by using the graph cut based segmentation. Finally, the training samples are input into a set of weak classifiers to learn the boosted classifier for generating the boosted saliency map, which is integrated with the initial saliency map to generate the final saliency map. Experimental results on two public image datasets demonstrate that the proposed model can achieve the better saliency detection performance than the state-of-the-art single-image saliency models and co-saliency models.
Proposed Saliency Model
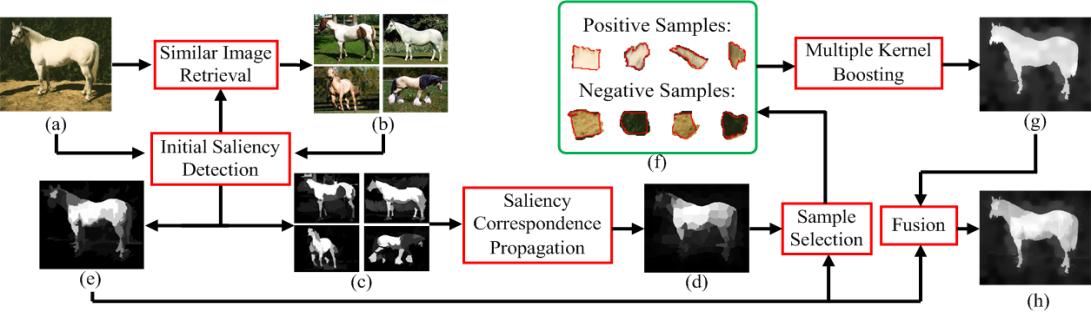
Illustration of the proposed saliency model. (a) Input image; (b) the retrieved images; (c) and (e) initial saliency maps; (d) correspondence saliency map; (f) training set; (g) boosted saliency map; (h) final saliency map.
Results
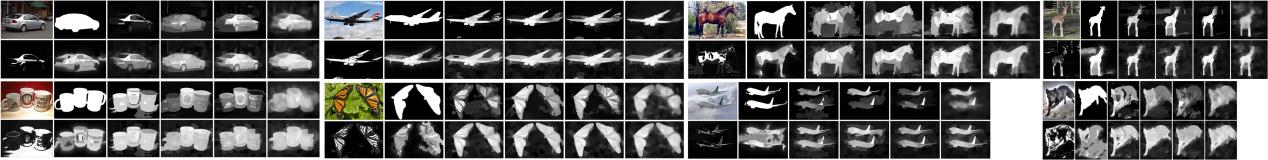
Visual comparison of saliency maps for some example images. For each example, in the top row from left to right: original image, ground truth, saliency maps generated using RC [9], ST [11], DRFI [14] and BL [16]; in the bottom row from left to right: co-saliency maps generated using CB [20] and CDR [25] and our saliency maps generated based on four different initial saliency models, i.e., Our-RC, Our-ST, Our-DRFI and Our-BL.
Quantitative Comparison
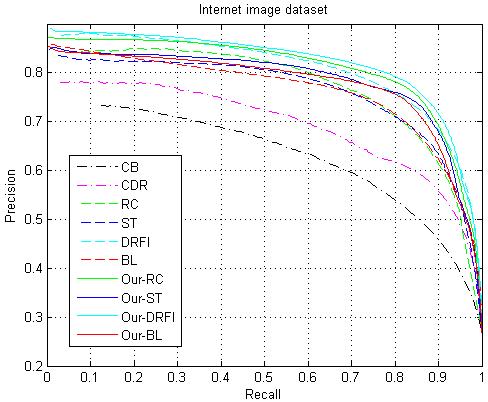
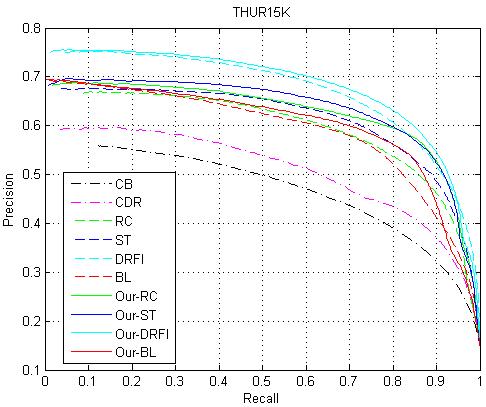
(better viewed in color). Precision-recall curves of different saliency models on the two datasets: Internet image dataset (left) and THUR15K (right).
Citation
L. Ye, Z. Liu, X. Zhou, L. Shen and J. Zhang, " Saliency detection via similar image retrieval," IEEE Signal Processing Letters, vol. 23, no. 6, pp. 838-842, Jun. 2016.
@ARTICLE{ Saliency Detection via Similar Image Retrieval_SPL2016,
author={ Linwei Ye, Zhi Liu, Xiaofei Zhou, Liquan Shen and Jian Zhang},
journal={Signal Processing Letters, IEEE},
title={ Saliency Detection via Similar Image Retrieval },
year={2016},
volume={23},
number={6},
pages={838-842},
doi={10.1109/LSP.2016.2558489},
ISSN={1070-9908},
month={Jun}
}.
Downloads
 |
"Saliency detection via similar image retrieval"
L. Ye, Z. Liu, X. Zhou, L. Shen and J. Zhang,
IEEE Signal Processing Letters, vol. 23, no. 6, pp. 838-842, Jun. 2016.
 [Paper] [Paper]
 [MATLAB Code] [MATLAB Code]
|